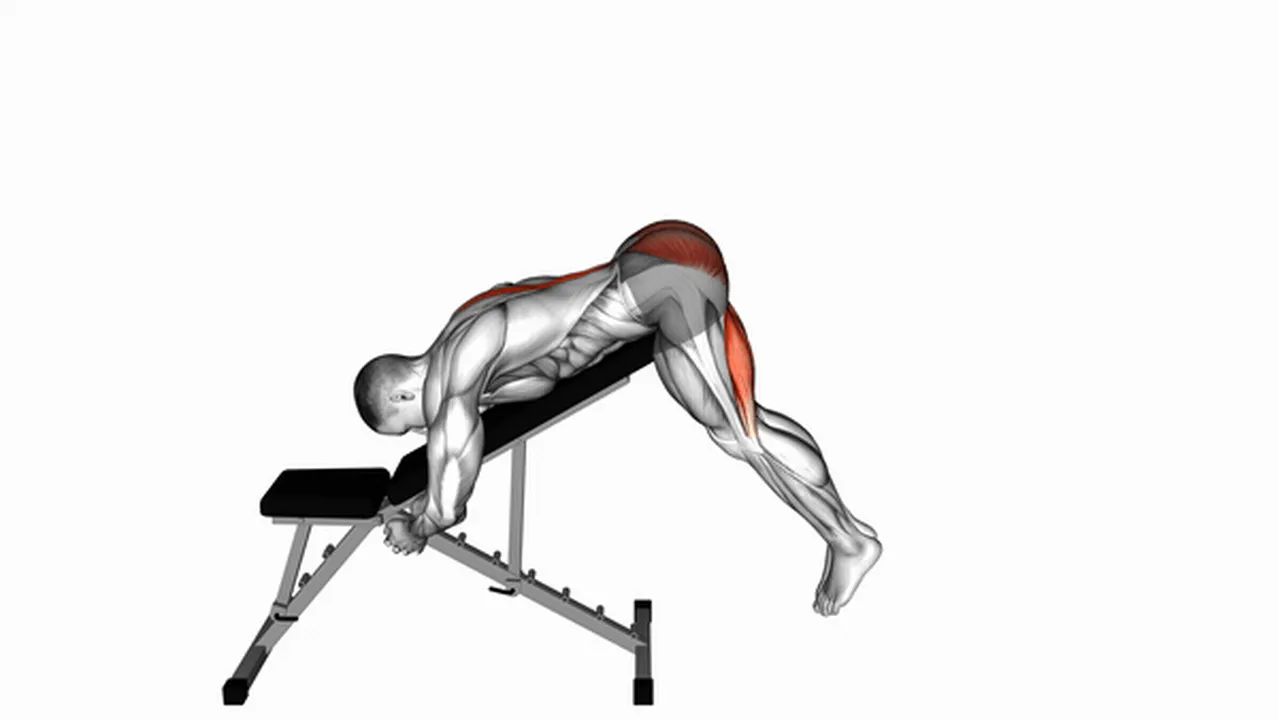
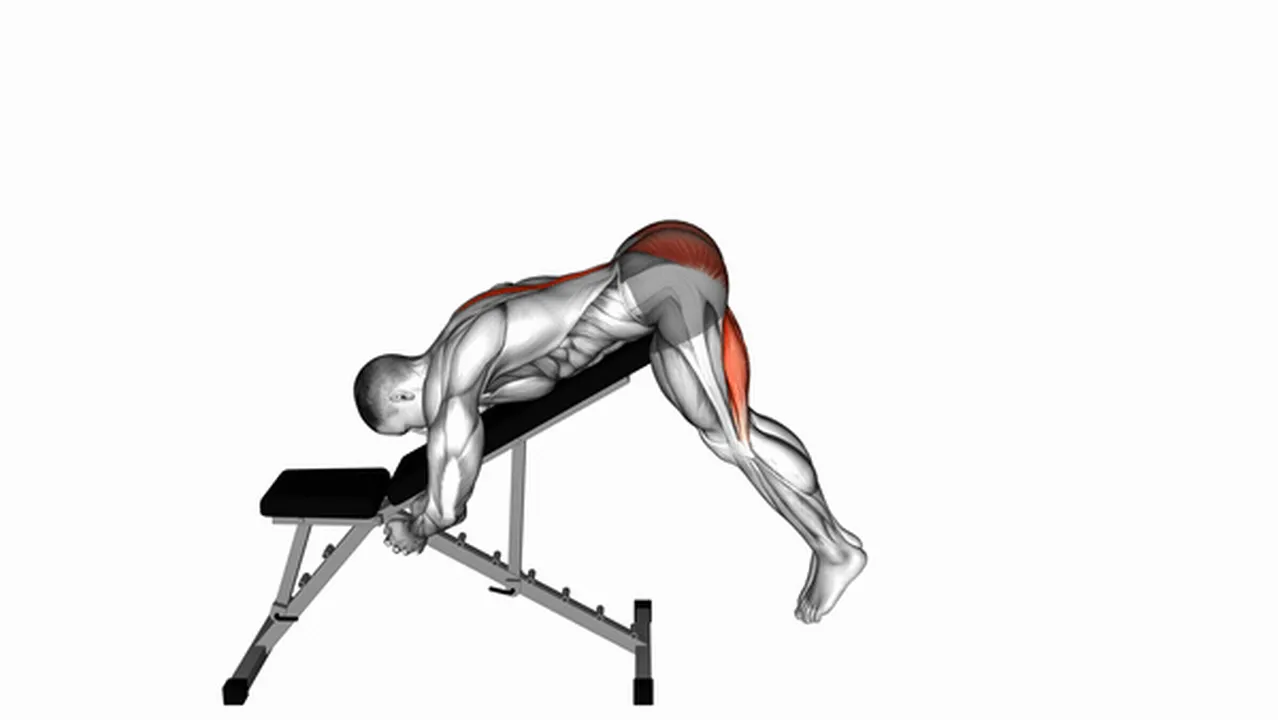
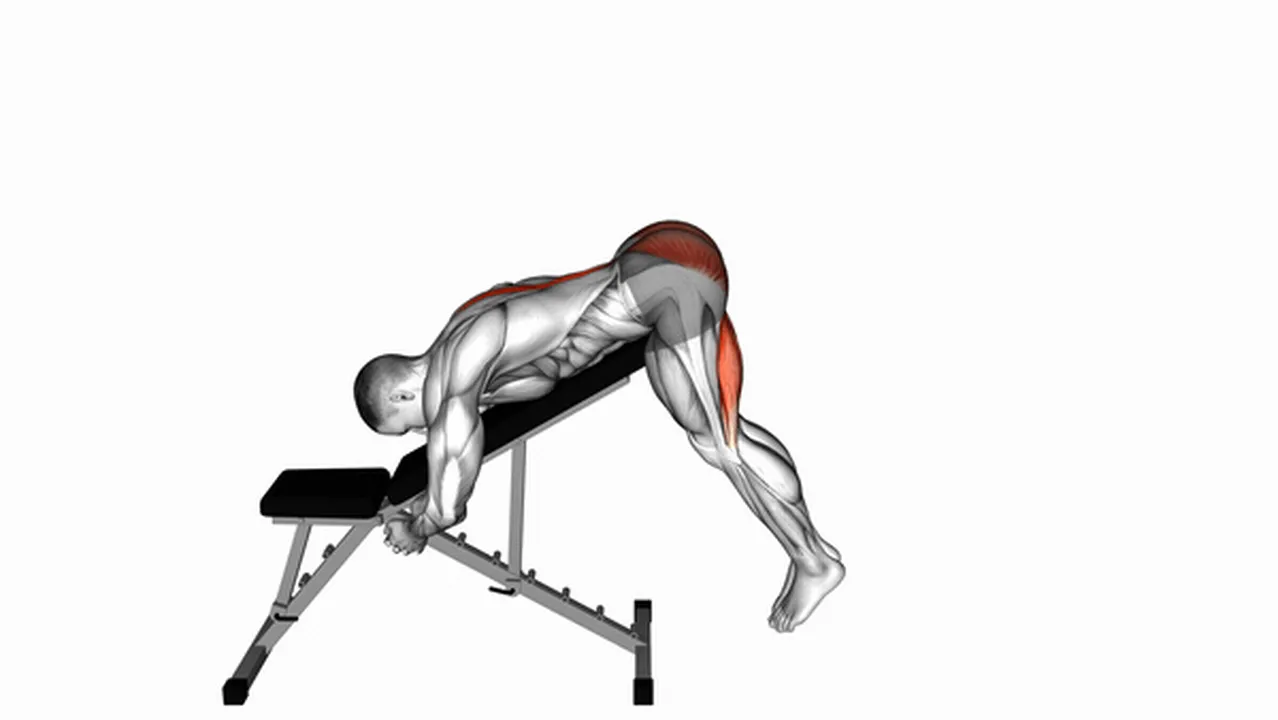
Disclaimer:
The routines and schedules featured on our website are for informational purposes only and do not constitute medical or professional advice. Individual preferences, goals, and daily routines may vary significantly. Please note that some product links within our content are affiliate links. While not all routines have been explicitly endorsed by the individuals mentioned, we strive to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information we provide.
Disclaimer:
BalancedRoutine(BR) does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Any information published on this website or by this brand is not intended as a replacement for medical advice. Always consult a qualified health or mental health professional with any questions or concerns about your mental health.